spring에서 모든 호출은 DispatcherServlet을 통과하게 되고 이후에 각 요청을 담당하는 Controller로 분배된다.
이때, 각 요청에 대해서 공통적으로 처리해야 할 필요가 있을 때
DispatcherServlet 이전에 단계가 필요하며 이 역할을 하는게 Filter다.

Spring Security도 인증 및 인가를 위해 Filter를 사용하며, FilterChainProxy를 통해서 상세로직을 구현한다.
Spring security에서 제공하는 인증방식: Form login
Form Login 기반 인증: 인증이 필요한 URL 요청 시 인증되지 않았다면 로그인 페이지를 반환하는 구조
내부에서 인증을 처리할 때 가장 많이 사용되는 방식으로 usernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter가 있다.
usernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 동작 방식
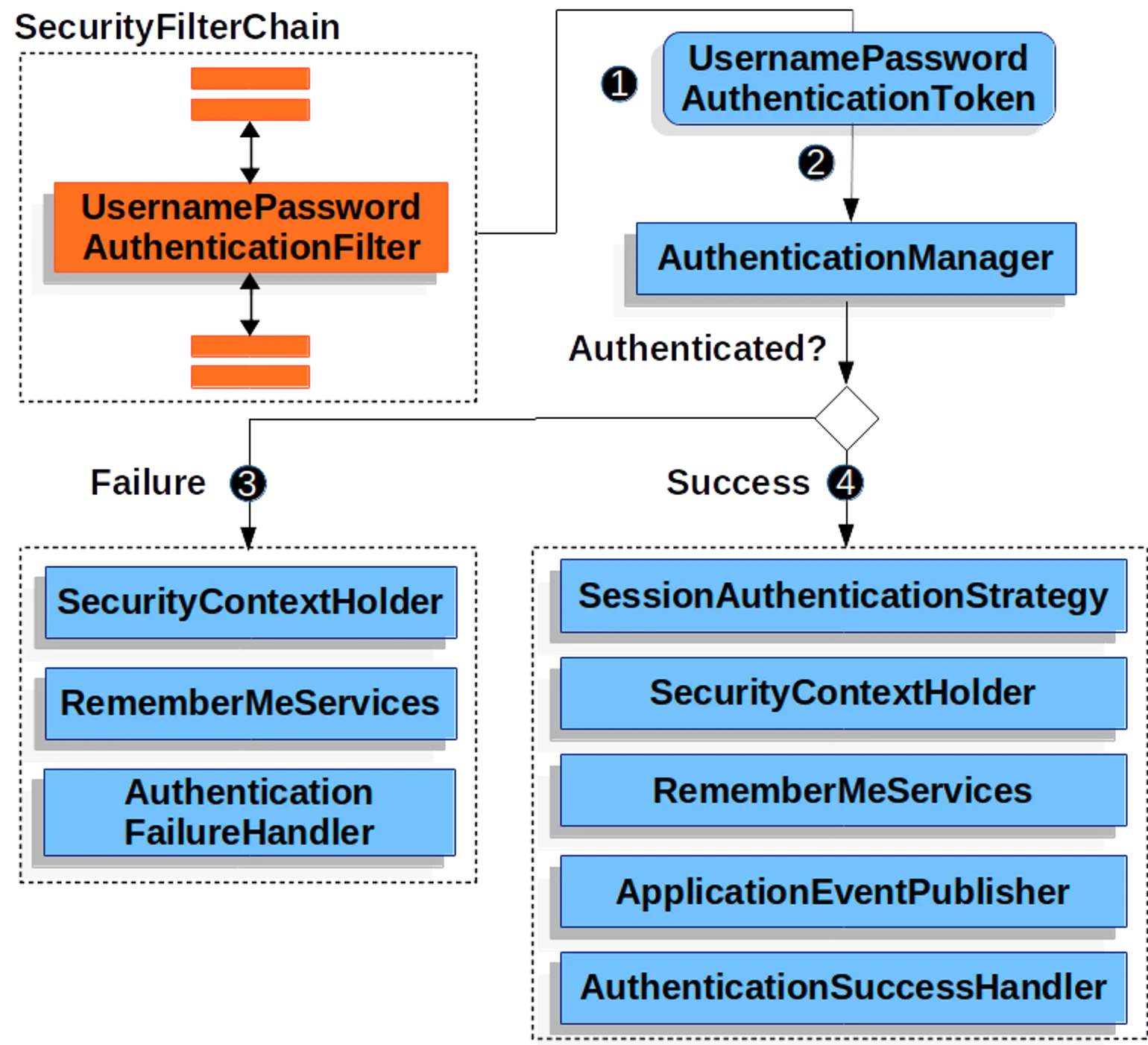
- 클라이언트가 SecurityFilterChain으로 유저네임, 패스워드 전달
- SecurityFilterChain이 usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 생성
- AuthenticationManager에게 토큰 전달. 매니저는 인증 시도
4-1 성공 시: SecurityContextHolder에 usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 저장
4-2 실패 시: SecurityContextHolder를 비운 후 loginpage로 redirect
SecurityContextHolder
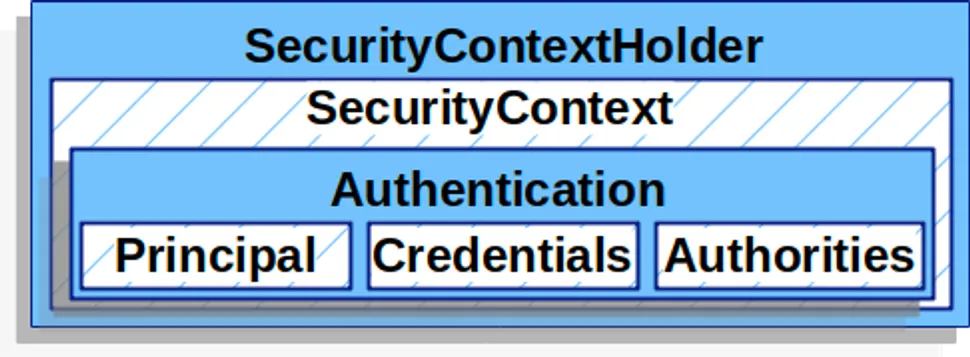
SecurityContext는 인증이 완료된 사용자의 상세 정보(Authentication)를 저장하는 공간이다
SecurityContext는 SecurityContextHolder 로 접근할 수 있다.
예시코드
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, credentials, authorities);
context.setAuthentication(authentication);// SecurityContext 에 인증 객체 Authentication 를 저장
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);
Authentication : 현재 인증된 사용자를 나타내며 SecurityContext에서 가져올 수 있다.
- principal : 사용자를 고유하게 식별할 수 있는 정보(아이디나 이메일 주소 등)
- credentials : 주로 비밀번호로 작성되며, 대부분 사용자 인증에 사용한 후 비운다.
- authorities : 사용자에게 부여한 권한을 GrantedAuthority로 추상화하여 사용한다.
<UserDetails>
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
UserRoleEnum role = user.getRole();
String authority = role.getAuthority();
SimpleGrantedAuthority simpleGrantedAuthority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(authority);
Collection<GrantedAuthority> authorities = new ArrayList<>();
authorities.add(simpleGrantedAuthority);
return authorities;
}
Authentication authentication = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userDetails, null, userDetails.getAuthorities());
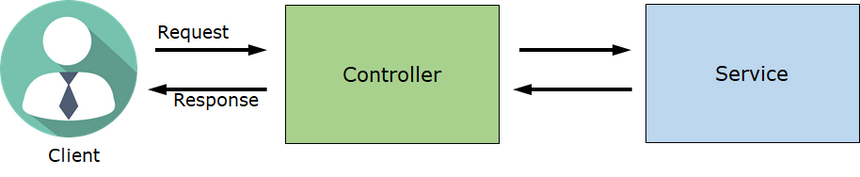
기존 service 구조
security 사용 시 구조
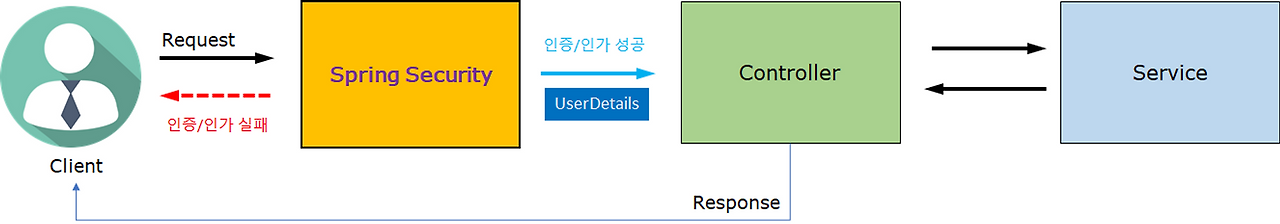
security는 Controller가 실행되기 전 Filter 에서 먼저 실행되기에 보안적인 측면과 속도 측면에서도 훨씬 좋다.
security 코드 예시
// 로그인 사용
http.formLogin((formLogin) ->
formLogin
// 로그인 View 제공 (GET /api/user/login-page)
.loginPage("/api/user/login-page")
// 로그인 처리 (POST /api/user/login)
.loginProcessingUrl("/api/user/login")
// 로그인 처리 후 성공 시 URL
.defaultSuccessUrl("/")
// 로그인 처리 후 실패 시 URL
.failureUrl("/api/user/login-page?error")
.permitAll()
);
예제코드 - security를 사용하지 않았을 때 인증 및 권한부여
if ( ... ) {
// 인증이 필요없는 기능들은 바로 요청 진행
} else {
// 나머지 요청은 인증 처리 진행// 토큰 확인String tokenValue = jwtUtil.getTokenFromRequest(httpServletRequest);
if (StringUtils.hasText(tokenValue)) {// 토큰이 존재하면 검증 시작// JWT 토큰 substring// 토큰 검증// 토큰에서 사용자 정보 가져오기
);
// 다음 Filter 로 이동
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Not Found Token");
}
}
}
예제코드 - security 사용 시 인증 및 권한부여
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorizeHttpRequests) ->
authorizeHttpRequests
.requestMatchers(PathRequest.toStaticResources().atCommonLocations()).permitAll()// resources 접근 허용 설정.requestMatchers("/api/user/**").permitAll()//**: 전부라는 의미.anyRequest().authenticated()// 그 외 모든 요청 인증처리
);
'CS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 동기 / 비동기 (Sync / Async) 와 블로킹 / 논블로킹 (Blocking / Non-Blocking) (2) | 2025.08.18 |
|---|---|
| [security] JWT와 Session의 차이 (0) | 2025.04.23 |
| [Spring]Front Controller, Dispatcher Servlet, Spring MVC 처리 Flow (0) | 2025.04.03 |
| [Backend] JSP (0) | 2025.04.02 |
| RestTemplate, WebClient, RestClient, FeignClient (0) | 2025.02.15 |